The Silent Struggle: Poverty Across Asia

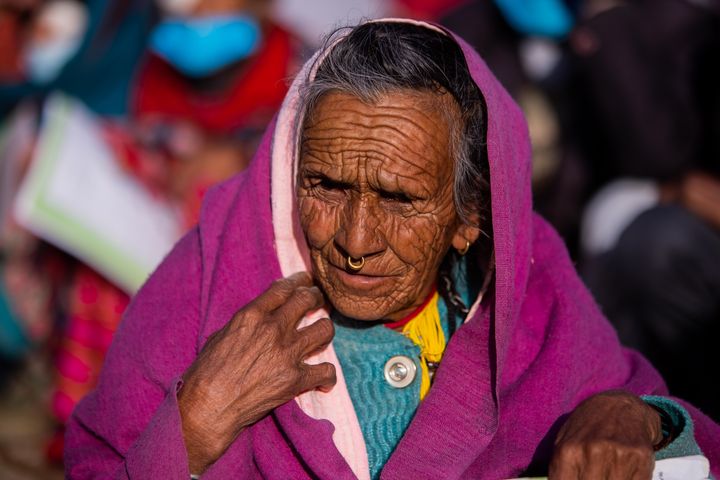
Poverty is a pervasive issue that affects millions of people across Asia, one of the most diverse and economically dynamic continents in the world. While Asia has experienced remarkable economic growth over the past few decades, the benefits have not been evenly distributed, leaving many individuals and communities trapped in a cycle of poverty. In this blog, we will explore the multifaceted nature of poverty in Asia, its underlying causes, and the efforts being made to address this pressing issue.
The Scope of Poverty in Asia
Asia is home to more than half of the world's population, with a wide range of cultures, economies, and social systems. Unfortunately, this diversity also means that poverty is complex and varies significantly from one region to another. Some common trends and challenges are, however, prevalent:
- Income Inequality: Income inequality is a critical issue across Asia. Rapid economic development has created a considerable gap between the rich and poor, with the wealth distribution often skewed towards urban centres. This leads to marginalized rural communities and overcrowded slums in many cities.
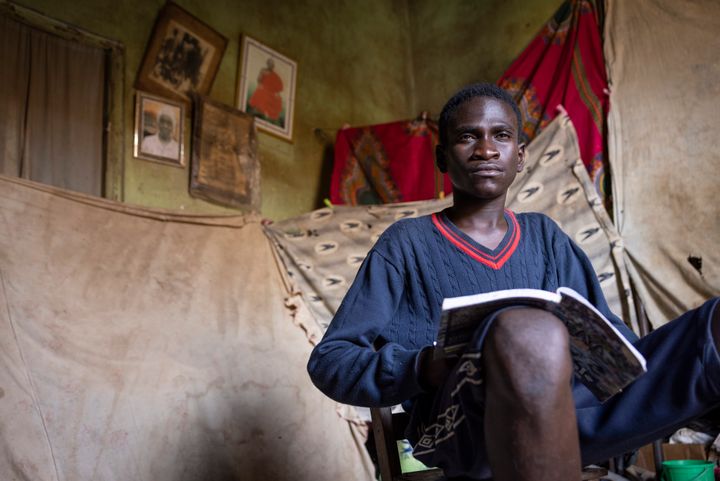
- Rural Poverty: A substantial portion of the Asian population still resides in rural areas and is dependent on agriculture for their livelihoods. Unfortunately, many of these communities lack access to modern farming techniques, quality education, and healthcare.
- Urban Poverty: As more people migrate to cities in search of better opportunities, urban poverty has become a growing concern. The lack of affordable housing, steady employment, and social services creates a breeding ground for poverty in urban areas.
- Child Poverty: A significant number of children across Asia suffer from poverty. Lack of access to quality education, proper nutrition, and healthcare can severely impact their future prospects and perpetuate the cycle of poverty.
- Gender Disparities: Gender discrimination is still a pervasive issue in many parts of Asia. Women often face limited access to education, employment, and healthcare, making them more vulnerable to poverty.
Root Causes of Poverty
The causes of poverty in Asia are multifaceted and interconnected:
- Lack of Education: Insufficient access to quality education perpetuates poverty. Many children, especially in rural areas, do not receive a proper education, limiting their future employment opportunities.
- Unemployment and Underemployment: High levels of unemployment and underemployment are common in many Asian countries, leading to low incomes and job insecurity.
- Healthcare Challenges: Poor access to healthcare services and sanitation facilities results in frequent health issues, driving families further into poverty.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: In many rural areas, the lack of basic infrastructure, such as roads, electricity, and clean water, hinders economic development.
- Corruption: Corruption within governments and institutions can divert resources away from poverty alleviation efforts and undermine trust in social safety nets.
Efforts to Combat Poverty
Governments, non-governmental organizations, and international bodies are working together to address poverty in Asia:
- Education Initiatives: Numerous programs aim to improve access to quality education, especially in rural areas. Scholarships and initiatives to keep children in school are being promoted.
- Microfinance: Microfinance institutions provide small loans to people in poverty, enabling them to start businesses or improve their existing ones.
- Social Safety Nets: Governments in Asia are increasingly implementing social safety nets to provide financial support to the most vulnerable populations, including cash transfer programs and food assistance.
- Skills Development: Vocational training programs equip individuals with the skills needed to secure better employment opportunities.
- Promoting Gender Equality: Initiatives to promote gender equality are essential to reduce poverty, as empowered women can contribute significantly to their families and communities.
Poverty remains a critical issue across Asia, affecting millions of people in various ways. It is not a problem with a one-size-fits-all solution, as it varies from region to region. Addressing poverty requires a multifaceted approach, including education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and addressing systemic issues such as corruption and income inequality. The progress made in combating poverty across Asia shows promise, but continued efforts, both at the governmental and societal levels, are essential to create a more equitable and prosperous future for all.



Comments ()