Poverty Rates In India - What are the Challenges?
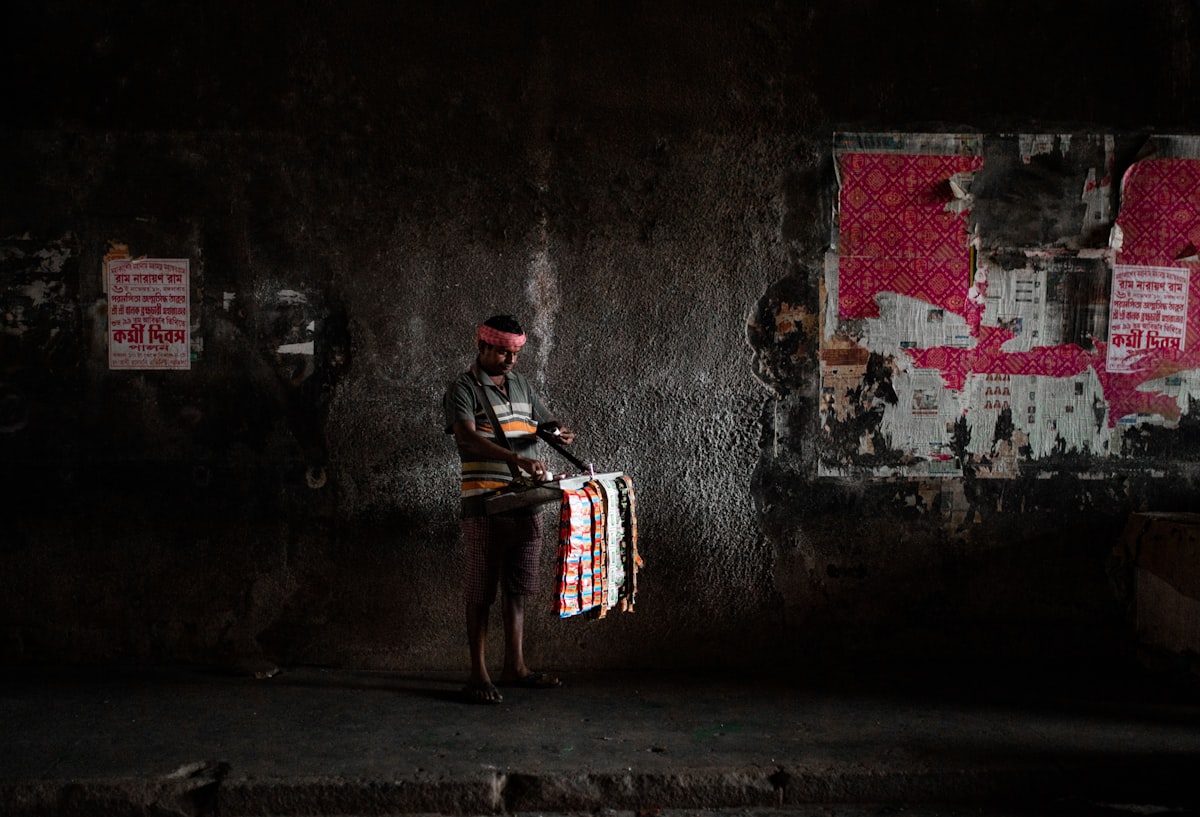

India is a country of contrasts. On one hand, it is a land of ancient traditions, rich cultural heritage, and natural beauty. On the other hand, India is also a country where poverty and inequality are widespread. Poverty rates in India have been a matter of concern for decades, and despite some progress, the problem remains acute.
According to the World Bank, India is home to one-third of the world's poor. In 2021, the poverty rate in India was estimated to be around 29.7%, which means that almost 370 million people in the country were living below the poverty line. The poverty line in India is defined as a daily income of INR 89 ($1.20) per person in rural areas and INR 134 ($1.80) per person in urban areas.
One of the main reasons for the high poverty rate in India is the large income inequality in the country. The top 10% of the population in India holds over 75% of the country's wealth, while the bottom 50% holds only about 5%. This means that the benefits of economic growth have not been distributed evenly, and many people have been left behind.
Another reason for the high poverty rate in India is the lack of access to basic services such as healthcare, education, and clean water. Many people in rural areas do not have access to proper healthcare facilities, and the quality of education is often poor. This limits the opportunities for people to improve their lives and break out of the poverty cycle.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a significant impact on poverty rates in India. The strict lockdowns and economic slowdown caused by the pandemic have led to an increase in unemployment and a decrease in income for many people, particularly those in the informal sector. The pandemic has also highlighted the inequalities in the Indian healthcare system, with many people unable to access proper healthcare during the crisis.
Despite these challenges, there have been some positive developments in recent years. The Indian government has launched several initiatives to address poverty, including the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA), which provides employment opportunities for rural households, and the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), which aims to increase financial inclusion by providing bank accounts to every household.
In conclusion, poverty in India is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders to address. While the Indian government has taken steps to alleviate poverty in the country, there is a lot more to be done to ensure that people living in poverty have access to basic services and opportunities.
Addressing poverty in India requires a long-term vision and sustained effort from policymakers, civil society organisations, and the private sector. Only then can India realise its full potential as a prosperous and inclusive society.
Tej Kohli is a philanthropist, technologist and investor.
Find out more about Tej Kohli: Tej Kohli the technologist investing in human triumph and Tej Kohli the London tycoon with a generous streak.
| Follow: Twitter | Instagram | LinkedIn | Facebook | YouTube |
Watch more:



Comments ()